The Risk Management Safety Net:
IV. Market Penetration of the Principle Crops
Efforts to improve market penetration for the principle crops have been very successful with 84 percent of all acres insured in 2012 (2012 is provided here because 2012 numbers were available for the principle crops) and 85 percent of all acres insured in 2011 compared to 74 percent in 2000 and only 38 percent insured in 1990. The purchase of buy-up levels of insurance coverage increased to 93 percent in 2012 and 2011 compared to 79 percent in 2000.
Many program changes have been made since 2000, including improved insurance products, additional availability of revenue coverage, additional subsidy, organic practices, and trend yield adjustments. Historically, the majority of efforts to improve market penetration were focused on these principle crops because they are widely grown in the U.S and public policy was directed to encourage participation in Federal crop insurance to avoid the need for ad-hoc disaster assistance. Improvements in principle crop market penetration from 2000 to 2012 can clearly be seen in the following graph.
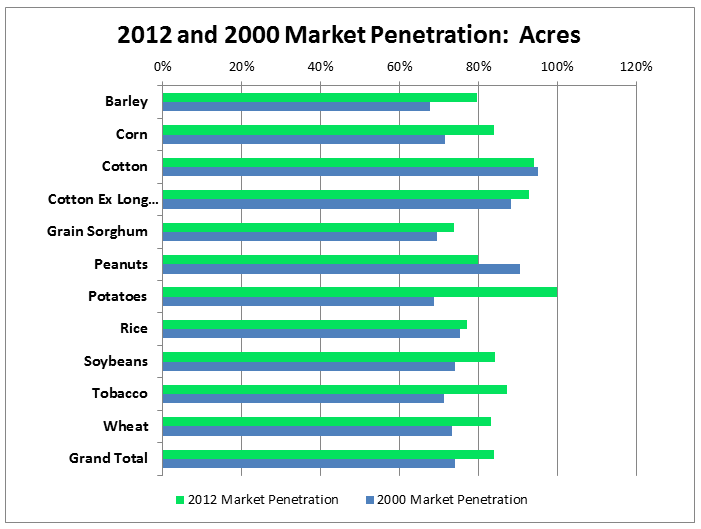
Coverage Levels Chosen By Crop for the Principle Program Crops
Some Federal crop insurance policies have large levels of participation at the Catastrophic (CAT) level of coverage, the lowest level of coverage offered, instead of at the higher levels of Buy-Up coverage.
Crop acres covered by buy-up levels of coverage have also increased substantially since 2000, increasing to 79 percent of insured acres in 2012 from 58 percent in 2000. Buy-up levels of coverage are levels higher than the fully subsidized catastrophic level and provide more insurance protection for the crop. The following chart shows the percentage of acres covered with buy-up levels of coverage for 2000 and 2012 for the principle program crops.
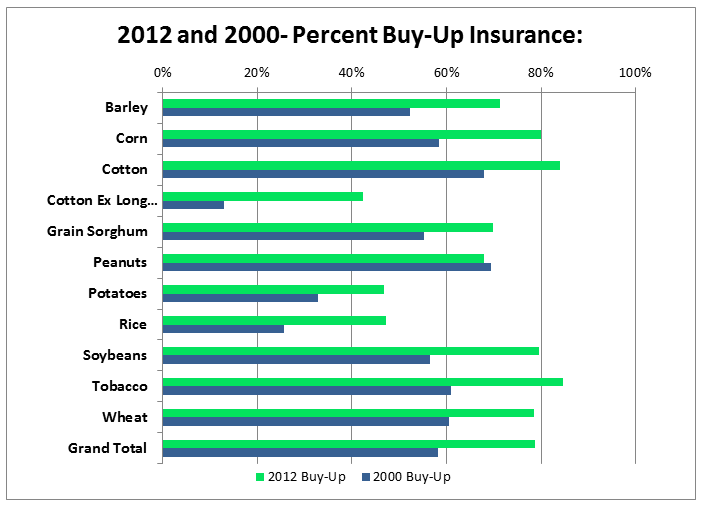
Participation for the principle crops, as shown in the previous charts, is high and the purchase of buy-up coverage is strong. While there may be some additional market potential, it is likely limited to a few crops.
Previous Portfolio Studies-Principle Crop Market Penetration in Southern States
Two states, Arkansas and Mississippi, were identified in a previous portfolio analysis, completed in 2004, as being inadequately served by Federal crop insurance products because the share of acreage covered by Buy-Up insurance was considerably lower than that of most other major crop producing states. A follow-up contracted study, completed early in 2008, was conducted to identify causes of low participation, potential product design problems and to obtain recommendations for program improvements to improve market penetration.
In 2012, Arkansas had 76 percent market penetration of the principle crops compared with only 66 percent in 2007 when the study was done. Arkansas also more than doubled its buy-up levels of coverage to 45 percent of the principle crops covered from 2007 to 2012. Mississippi had 91 percent market penetration of the principle crops, up slightly from the 89 percent in 2007. Mississippi buy-up levels also increased to70 percent from only 47 percent in 2007, so considerable progress has been made in capturing market potential and providing an effective risk management safety net to producers in these southern states since the study. Market penetration and buy-up levels of coverage for these states by principle crop are shown in the following table:
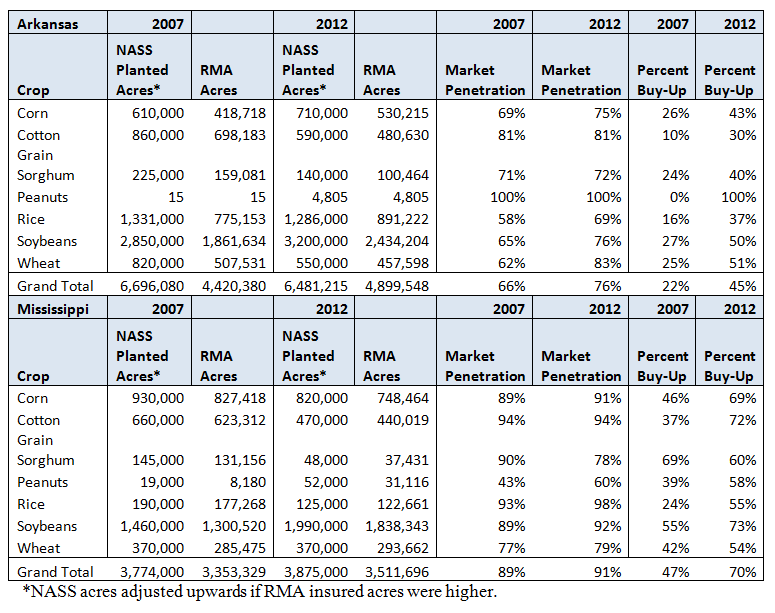
Program changes since the Arkansas/Mississippi study was conducted, some directly as a result of the study and others not, that likely responsible for the improvements in buy-up coverage amounts and market penetration are: (1) The separation of irrigated and non-irrigated types, to account for the fact that irrigation is a widely used practice, (2) A review and update of transitional yields, (3) Adjustment of final planting dates to better match production practices in the states, and (4) The enterprise unit subsidy was increased legislatively.
Contact Information
For more information, contact RMA Public Affairs.
|